Are you searching for MCQ Questions on Welding? Then you have come to the right place. Here, I will show you some multiple-choice questions on Welding. Also, there is one quiz on it.
At the end of this article, there is one “PDF” icon, with the help of which you can download this article.
Now let’s start the MCQ Questions on Welding.

MCQ Questions or Viva Questions on Welding
- The full form of MMAW is –
- mechanical material arc welding
- mechanical manual arc welding
- manual metal arc welding ✔️
- none of these
- The full form of S.M.A.W is _____.
- steel metal’s arc welding
- submerged material arc welding
- shielded metal arc welding ✔️
- none of these
- By welding, we can ________________.
- join two materials ✔️
- cut the slots
- reduce the diameter/length of the job piece
- none of these
- Which of the following is not a joining process
- welding
- brazing
- soldering
- casting ✔️
- In which of the following process, we can’t join two dissimilar materials?
- welding ✔️
- soldering
- brazing
- none of these
- In which joining process, the temperature is very high?
- welding ✔️
- brazing
- soldering
- none of these
- In which joining process, using filler material is a must?
- soldering
- brazing
- both 1 and 2 ✔️
- welding
- Electrode is coated to _____.
- protect the weld
- to remove rusting
- both 1 and 2 ✔️
- none of these
- In which of the joining process, does base metal melt?
- brazing
- soldering
- both 1 & 2
- welding ✔️
- In which joining process, filler material is optional?
- soldering
- brazing
- both 1 and 2
- welding ✔️
- The full form of G.M.A.W is
- Gun metal arc welding
- gas metal arc welding ✔️
- none of these
- Is electrode consumable in M.M.A.W?
- Yes ✔️
- No
- The chipping hammer is used to
- to remove the slag ✔️
- to hold the electrode
- to clean the work zone
- Which of the following is/are the defects of welding
- undercut
- porosity
- both 1 and 2 ✔️
- Which increases the porosity on the weld?
- Contaminated surface
- improper gas shield
- presence of moisture
- all of the above ✔️
- During welding, ______ray / rays is / are not produced.
- UV ray
- Infrared ray
- Gamma-ray ✔️
- all of these
- The name of the joint that has high corrosion resistance is _______.
- bolted joint
- riveted joint
- both 1 and 2
- welding joint ✔️
- In ______ welding, blacksmith fire produces heat
- projection welding
- spot welding
- forge welding ✔️
- none of these
- Through a chemical reaction, heat is produced in ______welding.
- resistance welding
- thermit welding ✔️
- tungsten arc welding
- none of these
- In oxy-acetylene welding, the temperature of the flame is ____degree Celsius.
- 200-300
- 1200-1300
- 2200-2300
- 3200-3300 ✔️
Quiz on Welding
You may consider this as a test of 24 marks. After completion of the test, you can check the answers and can come to know how much you are prepared on “Welding shop”.
Here is the quiz for you.
Overview
Are you searching for the explanation of some questions mentioned above, then go ahead and read the following text where you will get details about the welding shops.
Welding is a joining process by which we can join two similar materials with the application of heat or pressure or both.
The different types of welding
There are mainly 5 types of welding. These are Arc welding, friction welding, electron beam welding, laser welding, and resistance welding.
Arc welding
There are different types of arc welding. These are: metal inert gas welding (MIG), stick welding, tungsten inert gas welding (TIG) or tungsten arc welding, gas welding, metal active gas welding (MAG), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), submerged arc welding (SAW), flux cored arc welding (FCAW), shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), and plasma arc welding (PAW).
We primarily use filler material as joining metals. Aerospace Industry and Oil and Gas Industry use arc welding processes.
Friction welding
We can join the material using the heat created by mechanical friction. Mechanical friction produces heat that softens the materials. As a result, these two materials are joined.
The processes are named by the way in which joining occurs. Examples- are friction stir welding (FSW), friction stir spot welding (FSSW), linear friction welding (LFW), and rotary friction welding (RFW).
Electron beam welding
A beam of high-velocity electrons joins the materials. This joining process is the fusion joining process. The kinetic energy of these electrons transforms into heat.
The materials to be joined melt by this heat. This molten material joins the workpieces.
We perform the electron beam welding in a vacuum so that the beam does not dissipate.
Laser welding
The laser provides a concentrated heat that joins the workpieces.
We can get high welding speed in this welding process. As a result, we can use this process for high-volume applications. We can perform this process in the air too.
Resistance welding
It is a fast joining process.
This process is of two types- resistance spot welding and resistance seam welding.
Spot welding
- Clamp the workpieces.
- There will be a minor gap between the two workpieces.
- Heat delivered between two electrodes joins the workpieces.
Seam welding
- It is the same as spot welding.
- Here, there are rotating wheels in place of electrodes to provide continuous welding.
Out of these welding processes, the following welding processes are widely used:
- Gas metal arc welding
- Gas tungsten arc welding
- Shielded metal arc welding
- Flux-cored arc welding
Brazing
Brazing is a joining process by which we can join two metals with the help of filler material. The molten filler material flows into the joint. Here, the welding temperature is lower than that of the melting temperature of the brazing.
The melting temperature of the filler material is more than 4500c which is less than the melting temperature of the workpiece.
Soldering
Solder is a metal alloy. It consists of tin and lead. A hot iron melts it. The temperature of the iron raised above 6000F. After some time, it becomes cool and thus created a strong joint.
Hence, soldering is also a joining process by which we can join different types of materials with the help of molten solder.
The differences between welding, brazing, and soldering
| Welding | Brazing | Soldering |
| The metals to be joined must be of similar materials | maybe of different types of materials. | Different types of materials can also be joined. |
| The required temperature is very high | The brazing temperature is lower than the welding temperature but higher than the soldering temperature. | The soldering temperature is less than that of the welding and brazing temperature. |
| You may or may not use filler material. | You must use filler material. | Here also, you must use filler material. |
| Strongest joint among these joints. | Stronger than soldering but not strong as welding. | Weakest joint among these joints. |
| The processing temperature is 34000C | here it is 4500C | the temperature is 3000C to 3700C |
| Base material melts | does not melt. | here also does not melt. |
What is a butt joint?
The simplest joint is a technique by which we can join two same materials by simply placing their end together or placing both of them side by side.
What are the Welding Defects?
Welding defects are:
Weld crack
During the welding process, hot cracks can occur. The temperature at these cracks may exceed 100000C.
When the temperature of cracks goes down and the material becomes cool, cold cracks may appear.
High weld speed at low current and weld contamination is responsible for this defect.
Porosity
Weld metal contamination creates porosity. It looks like bubbles within which gases are trapped. With time, it becomes weak and may collapse.
A contaminated surface, improper gas shield, and the presence of moisture are the primary cause of this defect.
Undercut
A cavity or groove may form at the welding toe. This reduces the cross-sectional thickness of the base metal. As a result, the weld becomes weak.
High weld current, high weld speed, incorrect weld angle, and incorrect filler material are primarily responsible for this defect.
Incomplete fusion
A lack of proper fusion between the base metal and the weld metal causes incomplete fusion. As a result, a gap is created that is not filled with molten material.
Low heat, high weld speed, incorrect weld angle, and surface contamination are mainly responsible for this defect.
Incomplete penetration
Weld metal should flow throughout the groove of the metals. But, when it does not fully extend through the joint thickness, this defect occurs.
Too much space between the workpieces, large electrode diameter, misalignment, and improper joint mainly create this defect.
Slag inclusion
Immediately after welding, if it is not cleaned and another weld is passed, slags may deposit within the weld.
Spatter
Small particles of the weld attach themselves with the surrounding particles, especially in gas metal arc welding. No one can eliminate it completely.
Low voltage, high current, and too long arc are responsible for this defect.
Short Questions on Welding
What is M.M.A.W
Ans- M.M.A.W is manual metal arc welding.
What is the full form of S.M.A.W?
Ans -The full form of S.M.A.W is shielded metal arc welding.
Is electrode consumable in M.M.A.W?
Ans- Yes, it is consumable.
Which material is used for electrode coating?
A metal mixture, called flux covers the electrode. During welding, it gives off gases that prevent weld contamination. This introduces deoxidizers which create a slag. Thus the slag protects the weld and improves the arc stability.
Why the coating for the electrode is required?
Coating of the electrode is required to:
- Protect the weld
- Remove rusting
What are the precautions required while welding?
Precautions required are:
- Always wear a long-sleeved, non-flammable shirt.
- Wear- proper welding gloves.
- welding helmets.
- and face shield.
Job to be performed in the Welding shop
Job: making a butt joint on two M.S plates in a Welding shop
Here, students will learn how to make a butt joint on two M.S plates by electric arc welding.
Raw material diagram
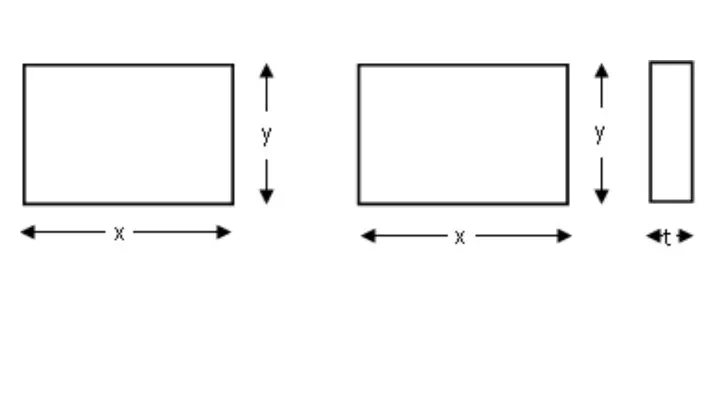
Finished job diagram
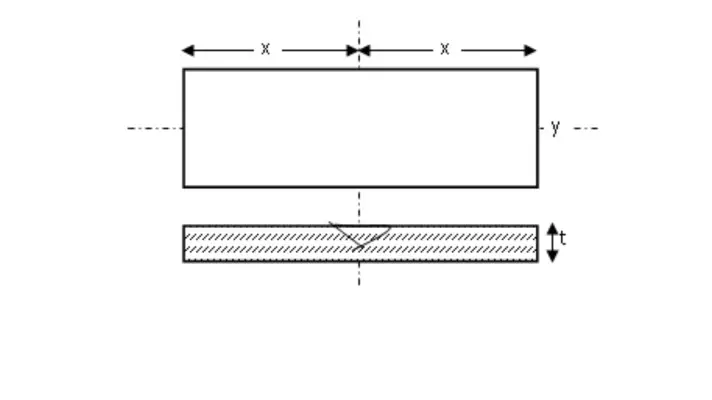
Name of the Tools
- Chipping hammer
- Tong
- Step-down welding transformer
- Welding table and fixtures
- Wire brush
- Gloves and apron
- Face shield
- Electrode holder
Procedure
Cleaning the raw material
- Clean the workpieces first.
- Then clean the welding table.
- Keep the workpieces on the table side by side.
Holding
- Take the electrode holder.
- Then insert an electrode within the electrode holder.
- Hold the electrode holder properly.
Welding
- Turn on the power switch.
- Then start welding.
- Draw a weld bead.
Chipping
- Take the chipping hammer.
- With its help, remove the slag from the workpiece.
Cleaning
- Take the wire brush.
- After that, clean the workpiece.
Finishing & Checking
- Check the finishing of the work pieces.
- Thus, you will get a welded joint.
Safety rules
- Always wear leather shoes, not sandals.
- Don’t wear loose clothes.
- Know the correct posture before welding the job piece.
- Hold the electrode in a proper way.
The multiple-choice questions mentioned here are the basic questions on Welding. I hope that the article-“Multiple-Choice Questions on Welding” will be helpful to you. If you want me to write the MCQ questions and answers on some other topics, please write in the comment box. If you find any contradictions in my answers, please let me know and give me a chance to improve myself. Thank you. Best wishes!



Chavan