Are you looking for Multiple-Choice Questions on Lathe Machine? If yes, then you are in the right place. In this article, there are some MCQ Questions on Lathe Machine that will help you in preparing for the viva for examinations.
There is also a Quiz on the Lathe Machine. At the end of this article, you may download the pdf format of this article by clicking on the pdf downloadable button.
Now, let us jump into the MCQ sections.
MCQ Questions or Viva Questions on Lathe Machine
- Which of the following operation performed on the lathe machine?
- material removing ✔️
- metal joining
- metal forming
- none of these
- The cutting tool used in the Lathe machine is _____.
- multi-point cutting tool
- single point cutting tool ✔️
- both of the above
- none of the above
- Which part of the Lathe Machine is called the Live center?
- Carriage
- Tail Stock
- Head Stock ✔️
- None of these
- Which part of the Lathe Machine is called the Dead center?
- Carriage
- Tail Stock ✔️
- Head Stock
- None of these
- Which of the following operation is called an internal turning operation?
- milling
- shaping
- tapping
- boring ✔️
- Tailstock in the Lathe machine is known as____.
- live center
- dead center ✔️
- tool post
- none of these
- The chuck is used to _____________________.
- hold the cutting tool
- hold the jaws
- hold the job piece ✔️
- none of these
- Lathe bed is made of ________.
- carbon steel
- stainless steel
- cast iron ✔️
- wrought iron
- The material of the cutting tool is______.
- high-speed steel ✔️
- cast iron
- carbon steel
- none of these
- The depth of cut for a cylindrical job piece is ____(where D1= outer diameter and D2= Inside diameter).
- (D1+D2)
- (D1+D2)/2
- (D1*D2)/2
- (D1-D2)/2 ✔️
- By turning operation we can____.
- reduce the length
- cut the slots
- reduce the diameter ✔️
- none of these
- By facing operation we can____.
- reduce the length ✔️
- cut the slots
- reduce the diameter
- none of these
Quiz on Lathe Machine
You may consider this as a test of 30 marks. After completion of the test, you can check the answers and can come to know how much you are prepared.
Overview
If you want more details about the Lathe machine, please go through the following text.
The Machine shop is the place where we can manufacture products that are made of metals.
A lathe is a machine that helps in shaping different objects. There is a job-holding device within the lathe machine. It is called a chuck. There are 3 or 4 numbers of jaws in the chuck. The job piece is being fixed within the chuck.
A lathe is a machine that rotates on the longitudinal axis along with the job piece to perform various operations like cutting, facing, deformation, etc. The common operations performed on Lathe machines are metal spinning, thermal spraying, woodturning, and metalworking.
In Lathe machine jobs, the job piece rotates and the cutting tool is moved by us.
In the Lathe machine shop, we can perform the following activities:
- Facing
- Turning
- Grooving
- Knurling
Out of these operations, while doing this job, students will learn the first three operations i.e. facing, turning, and grooving.
Lathe machine operations:
Facing
This is one type of cutting operation though cutting is not the purpose of this operation. The purpose of this operation is to make the surfaces of the job piece flat or smooth.
Hence, this is the first operation in any job to be performed in the Lathe machine. While making the surface finish smooth, some material of the job piece is removed. The front and back end surfaces of the cylindrical job piece are made smooth by this operation.
In this operation, the job piece rotates and it gets a radial feed.
Turning
Turning is a process in which we can remove the materials from the outer surfaces of the cylindrical workpiece along the longitudinal direction. Thus, we can reduce the diameter of the job piece as per our requirement.
There are various types of turning operations:
Straight turning
When we turn the work straight by making the workpiece rotate about the lathe axis and by feeding the tool parallel to the lathe axis is termed Straight turning.
Shoulder turning
If we have to make two or more different diameters in one job piece, the turning work we will make is termed shoulder turning. The change in diameter or step is known as the shoulder.
Rough turning
Initially, when we perform the turning operation, we aim to remove a large amount of material rapidly to produce a shape close to the desired shape. This is a rough turning.
Finish turning
Finish turning that follows rough turning, creates a smooth surface finish and produces the desired shape exactly.
Taper turning
Taper turning is a machining operation by which we can reduce the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece gradually from one part to another. The taper can be external or internal.
Contour turning
Contour turning is a machining operation by which we can make a three-dimensional reproduction of the shape of a template by controlling the cutting tool.
Eccentric turning
When we perform the turning operation of the workpiece not on the normal center axis, instead of at an offset to the center axis is called Eccentric turning.
Grooving
Grooving is a multi-step machining operation. It is a process by which we can form a narrow cavity of a certain depth on a cylinder.
Chamfering operation
We can bevel the ends of the job piece to look better and to get more accuracy by chamfering operation.
Knurling operation
When we need to produce a rough surface on the workpiece, we use a knurling tool and the operation is named the knurling operation.
Thread cutting operation
It is a machining operation by which we can produce a helical groove on the cylindrical surface of the job piece. In this operation, we feed the tool longitudinally.
Drilling operation
We can make a hole in the job piece by this operation.
The drill tool is fitted with the tailstock spindle. We can move the tailstock towards the job piece.
Boring operation
When we need to enlarge the diameter of the existing hole, we use a boring tool that is fitted on the tailstock. The operation is known as the Boring operation.
Reaming operation
When we need to finish an existing hole to the required size, we perform this by reaming the tool. The operation is known as Reaming operation.
Spinning operation
Through this operation, we can change the shape of the job piece by deforming it over a pre-shaped mold. It changes the shape of the metal to reflect that of the mold on which it is spun.
Tapping operation
We can create internal threads within a hole by taps. This operation is known as the tapping operation.
Parting off operation
Through this operation, we can make it apart from a bar. This part is required for other operations. The bar is held in a chuck and then one end of the bar is cut off from the rest of the bar. Thus, we can make a part of this operation.
Machining parameters
Cutting speed
Cutting speed is the speed at which the job piece moves with respect to the cutting tool. It is expressed in ft/min or m/min.
Vc=(πD0 N)/1000
D0-outer diameter of the cylindrical job piece.
N- r.p.m of the spindle.
Di– inside diameter of the cylindrical job piece.
Depth of cut
How wide and deep, the tool cuts into the workpiece is known as the depth of cut. It is measured in millimeters or inches.
d=(D0 – Di)/2
Feed rate
The amount of material in mm is fed per revolution during the machining operation is termed as feed rate(mm/min). For the Lathe machine, the cutter is fed against the workpiece.
Feed rate, fr = fN
f= feed per revolution.
Tool geometry
The design of the edge of the cutting tool is termed tool geometry has a great influence over the following things:
Chip formation
Heat generation
Tool wear
Surface finish
Machine/spindle power
Power is the product of force and velocity in linear motion and the product of torque and rotational velocity in rotational motion.
If we increase the cutting speed, cutting forces will increase. Thus, the peak power required by the machine spindle will increase.
Coolant
The main purpose of a coolant is to provide a cooling effect on the workpiece at the time of the machining process and also to lubricate the work surfaces.
Machining time(min)
tm=L/fr =L/fN
L= length of cut.
Material removal rate(MRR)
Material removal rate, MRR=vfd
We are giving an example so that students can understand the need for the machining parameters and how to calculate those parameters:
Numerical Question on Lathe machine
A cylindrical stainless steel rod with length L = 70 mm, diameter D0=18 mm is being reduced in diameter Df=12 mm by turning on a lathe. The spindle rotates at N= 400 rpm and the tool is traveling at an axial speed U = 200 mm/min.
Calculate:
- The cutting speed V (maximum and minimum)
- The material removal rate(MRR)
- The cutting time t
The power required if the unit power is estimated to be 4w.s/mm3
Solution:
Maximum cutting speed is at the outer diameter, D0, and is obtained from: Vmax=3.14x18x400=22608 mm/min
Cutting speed at the inner diameter = 3.14x12x400= 15072 mm/min
Total depth of cut,d is =(18-12)/2=3 mm
Feed is f= U/N=200/400=0.5 mm /rev
MRR=3.14xDavgxdxfxN= 3.14x15x3x0.5×400=28260mm3/min=471 mm3 /sec
Cutting time, t = (L/f.N)=(70/0.5×400)=0.35 min
The power required, P= unit power x MRR
- P= 4 (w-sec/ mm3)x471(mm3/sec)=1884 w
Job by Lathe machine: Making a Round-Headed Peen
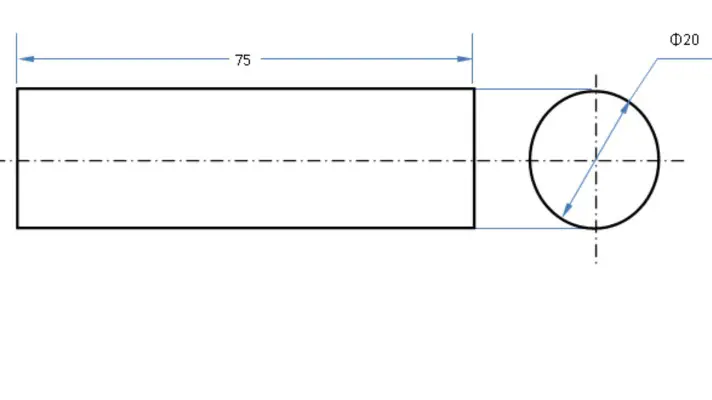
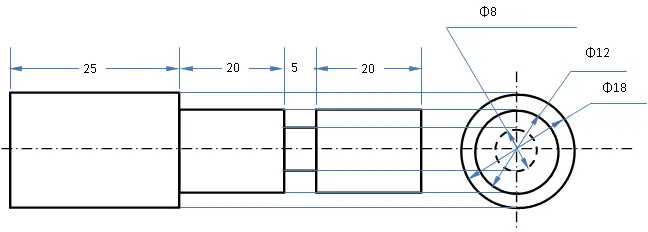
Diagram
Tools required:
- Steel rule1’
- Outside caliper
- Ball peen hammer
- Chak
- Turning tool
- Grooving tool
- Tool holder
- Lathe machine
Procedure:
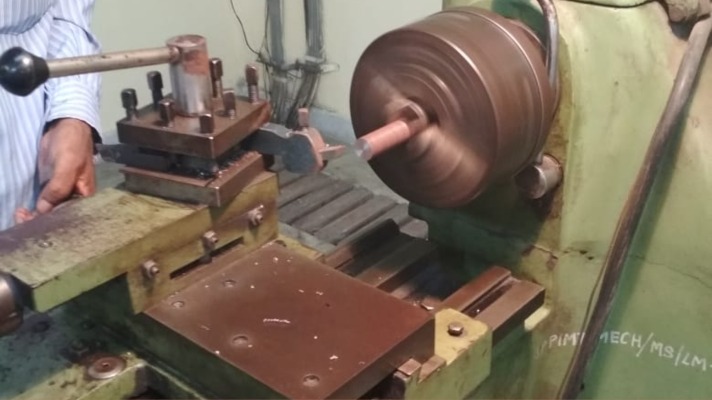

Facing
Take the cylindrical job piece.
Then, fix the job piece in the chuck with the help of a chuck key.
Remove the chuck key from the chuck. Then, switch on the machine.
Shift the cutting tool towards the job piece.
Set the depth of cut through the compound slide and feed through the cross slide.
Then, move the cutting tool slowly. As a result, it will move across the diameter of the cylindrical job piece.
Thus, the front surface will become smooth. This is called a facing operation. Therefore, in this operation, the length of the job piece will be reduced.
Then, take out the job piece from the chuck after switching off the machine.
Then, repeat this process for other ends.
In this operation, the diameter of the job piece will remain the same i.e. 20 mm and the length will reduce from 72 mm to 70 mm.
Marking
Next, you have to mark the length for which you will reduce the diameter.
Say, at present, the diameter of the job piece is the same throughout the length and it is 18mm.
First, you have to reduce the diameter of the first 45 mm length of the job piece. So, mark 45 mm in length with chalk.
Turning
Reduce the diameter from 20 mm to 12 mm by turning operation.
Then, fix the job piece in the chuck.
After that set the depth of cut through the cross slide and feed through the compound slide.
When the depth of cut and feed have been set. switch on the machine. Then, move the cutting tool slowly toward the job piece.
As a result, the cutting tool will remove the material from the circumference of the job piece and it will move across the length.
Grooving
For grooving operation, 20 mm away from one edge mark by chalk.
Set the grooving tool.
Then set the depth of the cut.
After that, switch on the machine.
Turning
Reduce the diameter of 25 mm length from other ends by turning operation (same as mentioned before).
Finishing and checking
Check the finishing of all the surfaces. If required, perform the required machining operation.
Parts of the Lathe machine
Bed
On which the main parts of the machine take rest.
Headstock
Generally, it is located on the left side of the Lathe machine. It carries a chuck, spindle, speed control levers, and feed controllers. The spindle is inside the headstock. As the headstock carries moving parts, it is called the living center.
Tailstock
Generally, it is situated on the right side of the Lathe machine. It supports one end of the workpiece when it is too long.
As it does not carry any moving parts, it is called the dead center.
Chuck
It is equipped with 3 or 4 numbers jaws. For machining the workpiece of regular surfaces, we require a 3-jaw self-centered chuck. These jaws hold the workpiece. We can move the jaws with the help of the chuck key.
Spindle
There is a spindle within the headstock. On the spindle, the chuck is mounted. The spindle is connected to the motor. When the motor runs, the spindle rotates. As a result, the chuck rotates and the workpiece also rotates.
Compound slide
It is located on the compound rest. We can set the depth of cut for the facing operation and feed for the turning operation.
Cross slide
It is located in the carriage. You can set the depth of cut for turning operation and can set the feed for facing operation
Tool post
It rests on the carriage. It contains a turning tool, a grooving tool, etc.
Carriage
It is located between the headstock and tailstock. It carries a compound rest, cross slide, tool post, saddle, and apron.
Feed rod
It helps in moving the carriage from left to right or from right to left.
Lead screw
While threading, we require to move the carriage. The lead screw helps in moving the carriage automatically during threading operation.
Chip pan
Chip pan collects the chips that are produced while performing machining operations.
Hand wheel
You will operate the handwheel for moving cross slide, carriage, etc.
Common Safety rules
- Always wear leather shoes, not sandals.
- Don’t wear loose clothes, wrist a watch during the job.
- Don’t touch the machine in absence of Technical Assistants.
- Stand at a safe distance.
Precautions for this job
- Before switching on the machine, make sure the following:
- The center point of the job piece is in line with the lathe axis.
- Fix the job piece tightly within the chuck.
- Remove the chuck key from the chuck.
2. Keep patience while setting the least count.
I hope that the Multiple-Choice Questions on Lathe Machine will help you a lot. If you need MCQ questions on some other topic, please write in the comment box. I will write about that too. Thank you. Best wishes!



Thank you so much mam it really helped me a lot
Thanks Sutanika.
Thanks so much!